
Lupus Erythematosis
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Collagen Vascular Diseases
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Scleroderma
Rheumatoid Lung
Polyarteritis Nodosa

Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lungs and pleura involved more often inlupus than other collagen vasculardiseases
Type III immune complex phenomenon

LupusClinical-1
Anti-nuclear antibody present in 87%
LE cells in 78%
Rheumatoid factor in 21%
False + test for syphilis in 24%

LupusClinical-2
Skin changes include
Butterfly rash
Alopecia
Photosensitivity
Raynaud's
Sjogren’s Syndrome frequent

LupusThoracic Changes
Pleural effusions
Discoid atelectasis at both bases
Pericardial effusions
Lupus pneumonitis

Drug-induced Lupus -1
Hydralazine
Pronestyl (procainamide)
Dilantin
INH
Account for 90% of cases of drug-induced lupus

Drug-induced Lupus -2
Pleuroparenchymal changes morecommon than SLE
Does not involve kidney
Disappears if drug is stopped

LupusX-ray-1
Pleural effusion is most common lungmanifestation
Secondary to pleuritis
Usually bilateral and small but may be verylarge
If unilateral, more often on the left

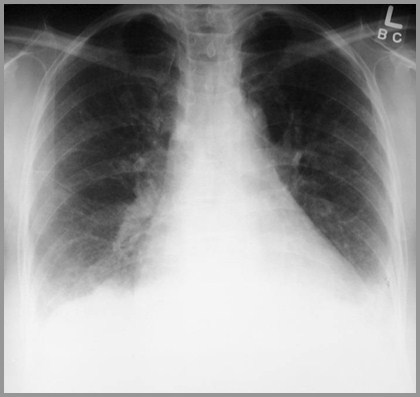
Bilateral pleural effusions in Lupus

LupusX-ray-2
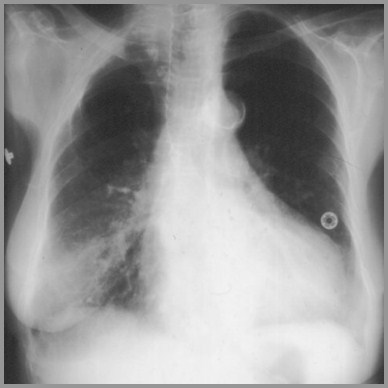
Patchy areas of consolidation at lungbases, especially peripherally
May be 2° to infection (common) or lupusinfiltrates (uncommon)
Discoid atelectasis common
Massive pulmonary hemorrhage mayoccur

Airspace disease in the right lower lobesecondary to Lupus

LupusX-ray-3
Cavitary nodules may occur
More common in RA
Cardiomegaly 2° to
Pericardial effusion
Cardiomyopathy
Diffuse interstitial fibrosis does not occurin SLE

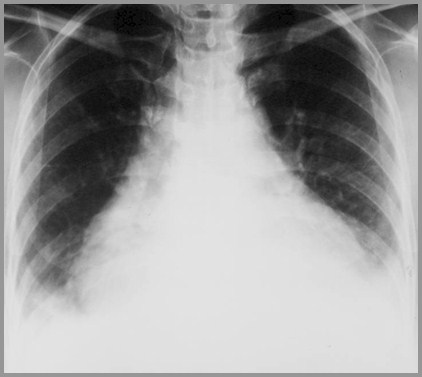
Pericardial effusion and bilateral pleuraleffusions

Think of SLE:
Pleural effusion
Discoid atelectasis
Patchy infiltrates at the bases
DDx: thromboembolic disease

The End